Trusted By Hundreds of Businesses Since 2010
Full-Scale Marketing Team Access
Starting at $95 Per Month
Delivering premium full-scope marketing production for less than half the average agency cost.

GRAPHIC DESIGN
Differentiate your brand, convey your level of quality, and establish a memorable presence with sophisticated visuals.
CONTENT MARKETING
Use strategic content and clever copy to convert your target audience into customers and customers into loyal advocates.


WEB DEVELOPMENT
Establish a powerful online foundation for your marketing program through conversion-focused UX/UI design.
SOCIAL MEDIA
Stay relevant on social media by delegating your post designing, content crafting, scheduling, and engagement efforts.
DIGITAL ADS / PPC
Hyper-target your audience and use modern advertising strategies to guide them through every phase of your marketing funnel.
The Perfect Marriage of
Modern Marketing Solutions
We’ve combined on-demand flexibility with the coordination, consistency, and quality of a top-tier agency.

Specialized
Specialized marketing teams overseen by your dedicated marketing manager.
Flexible
Fluidly scale your project volume up or down without penalty.
Equitable
You own all of the accounts, source files, and other assets used on your projects.

Low-Risk
Our terms are month-to-month with no minimums and no penalties.
Working as a Fluid Extension
Of Your In-House Team
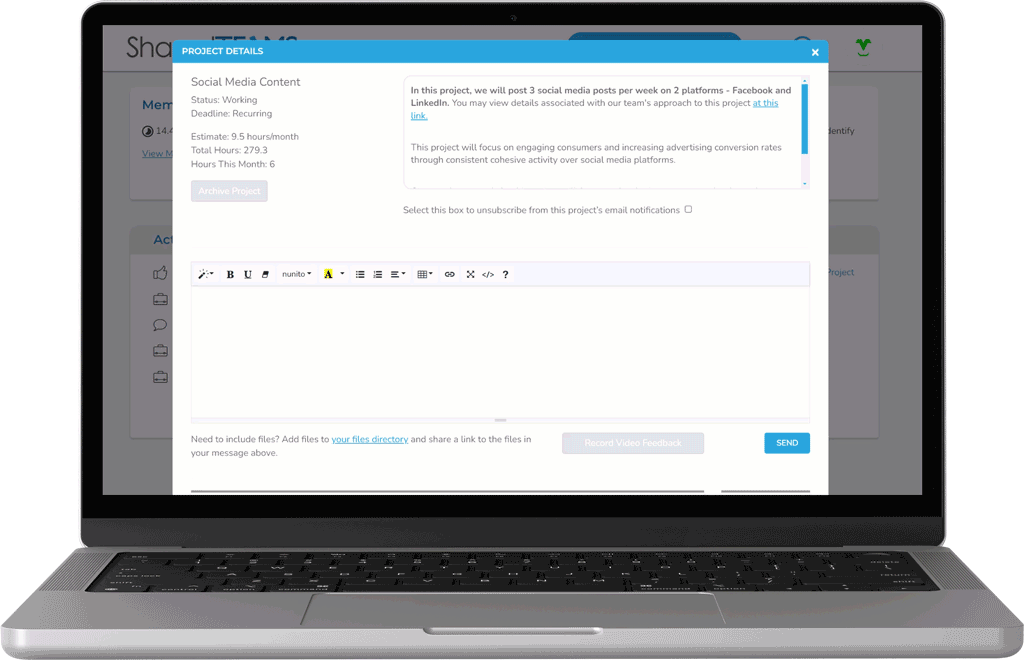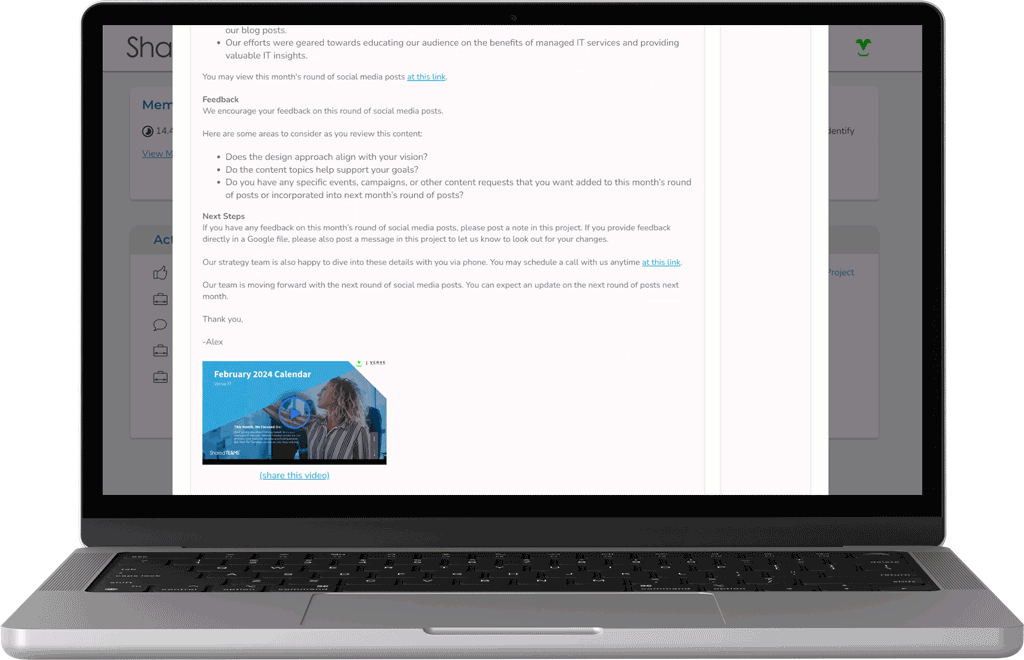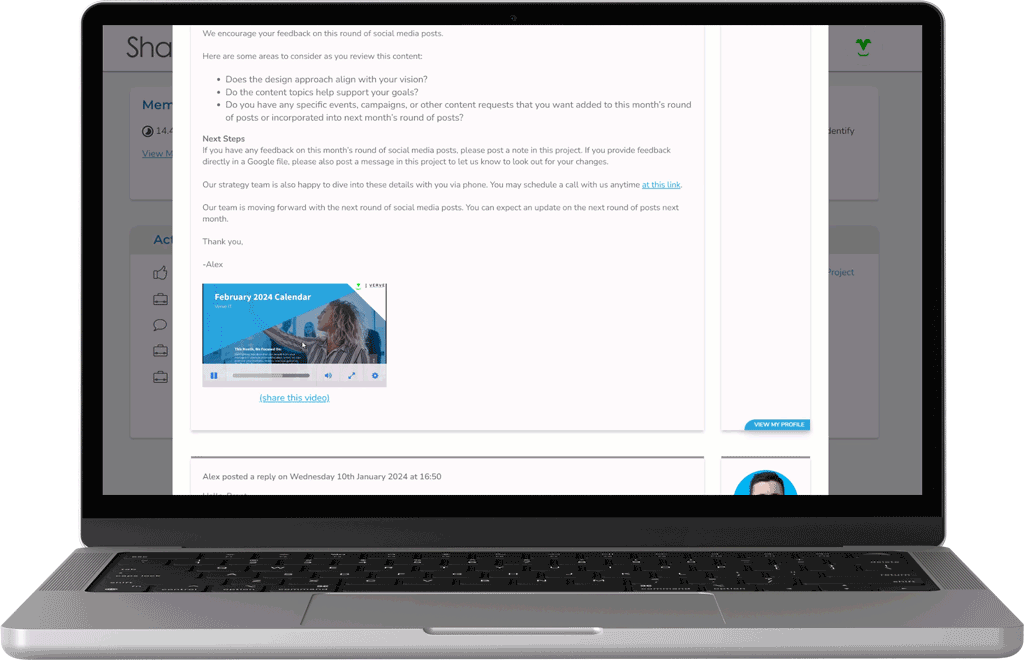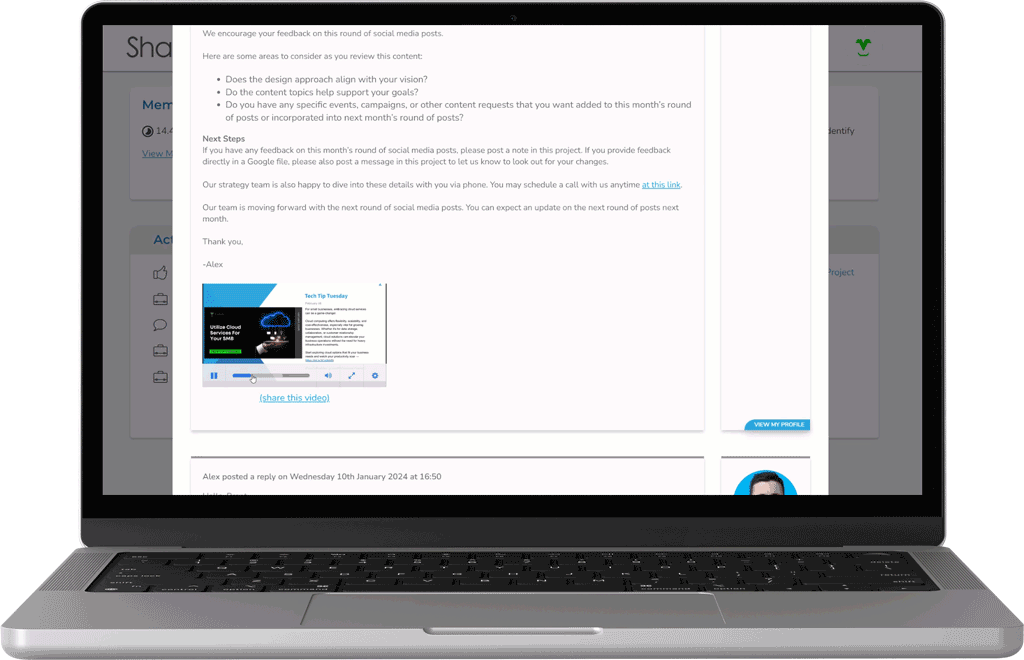
Receive Real-Time Progress Updates
Stay in the loop with project progress 24/7 by reviewing real-time project statuses and collaborating with our team through our custom platform.
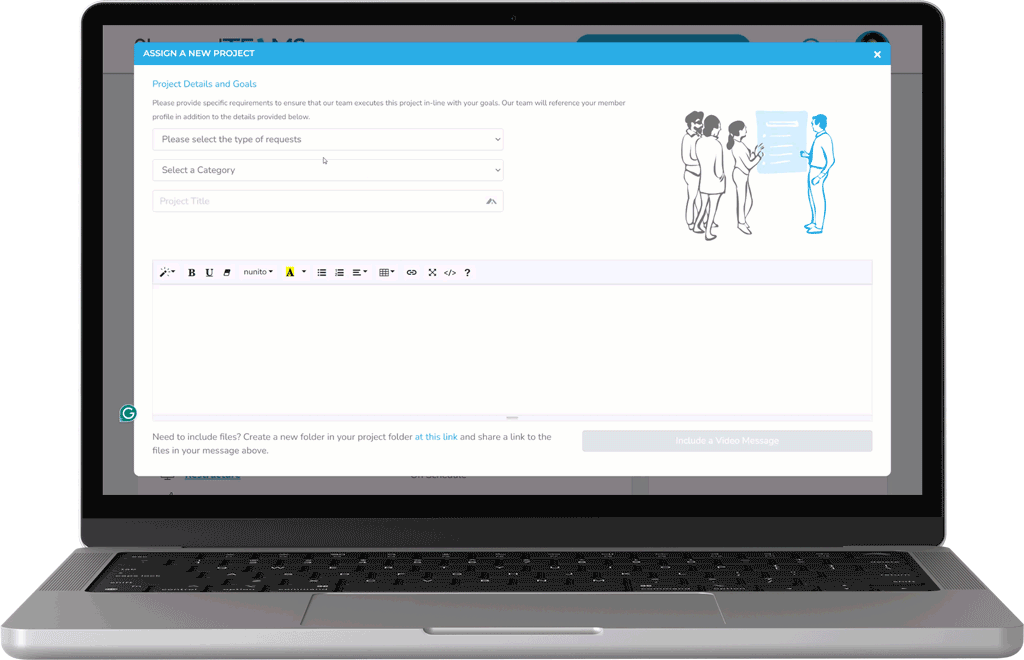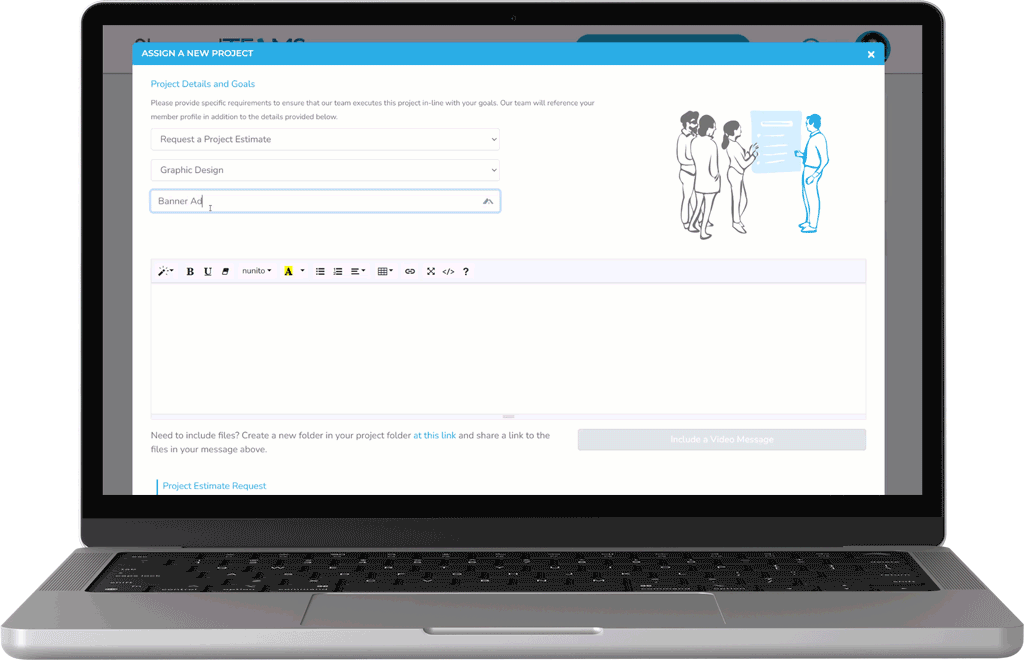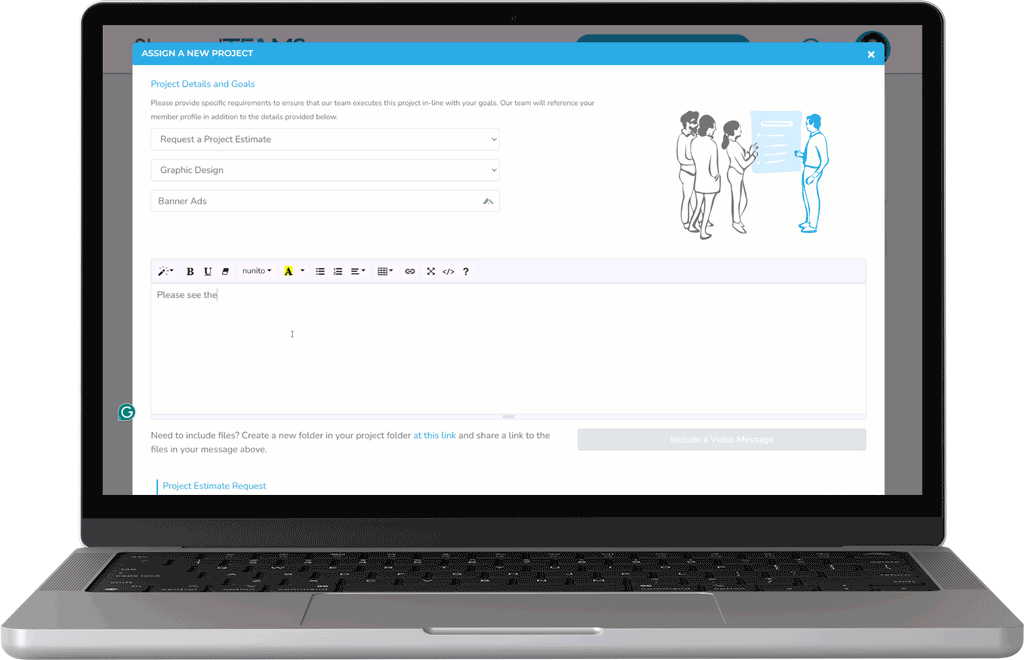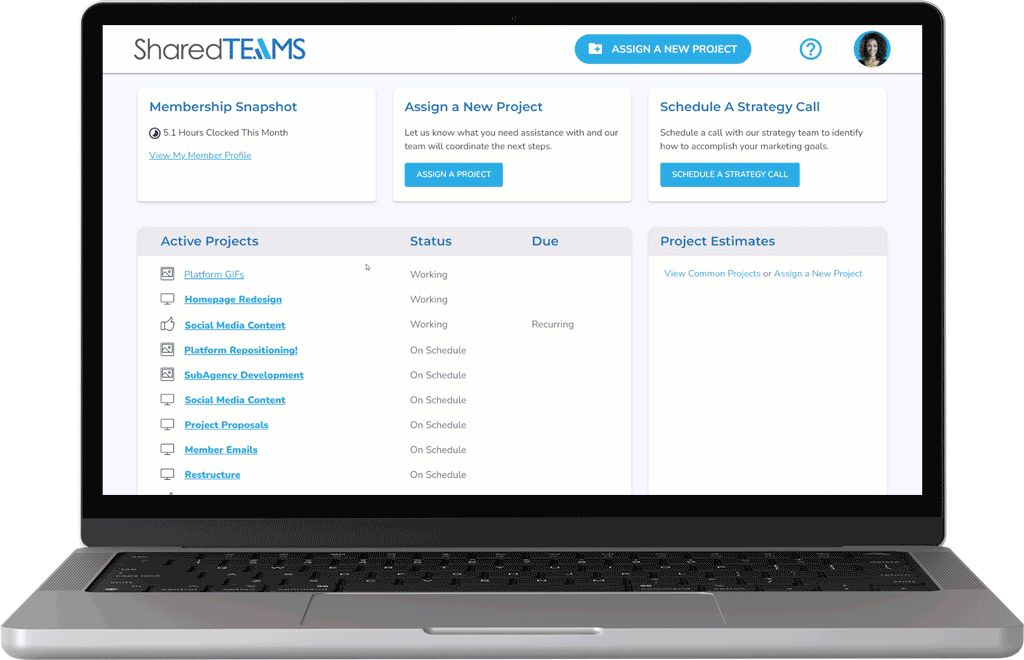
Easily Delegate Marketing Activities
Our custom project assignment and estimate request system gives you direct access to outsource projects when you need the support.
Using Modern Feedback Tools
Collaborate with our team using your preferred combination of video calls, in-platform chat, or recorded video feedback.
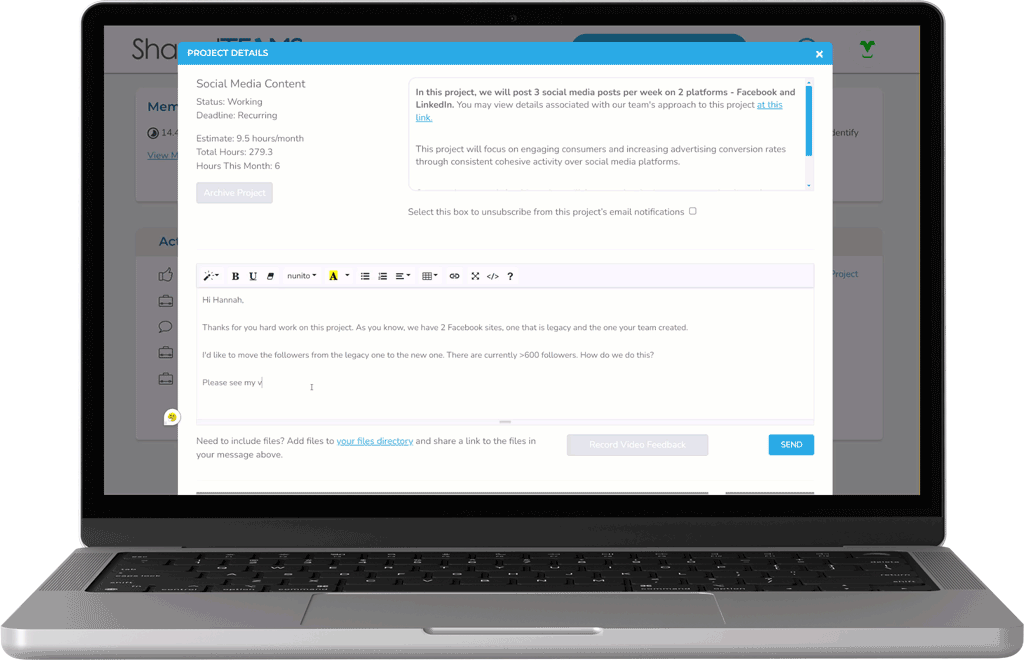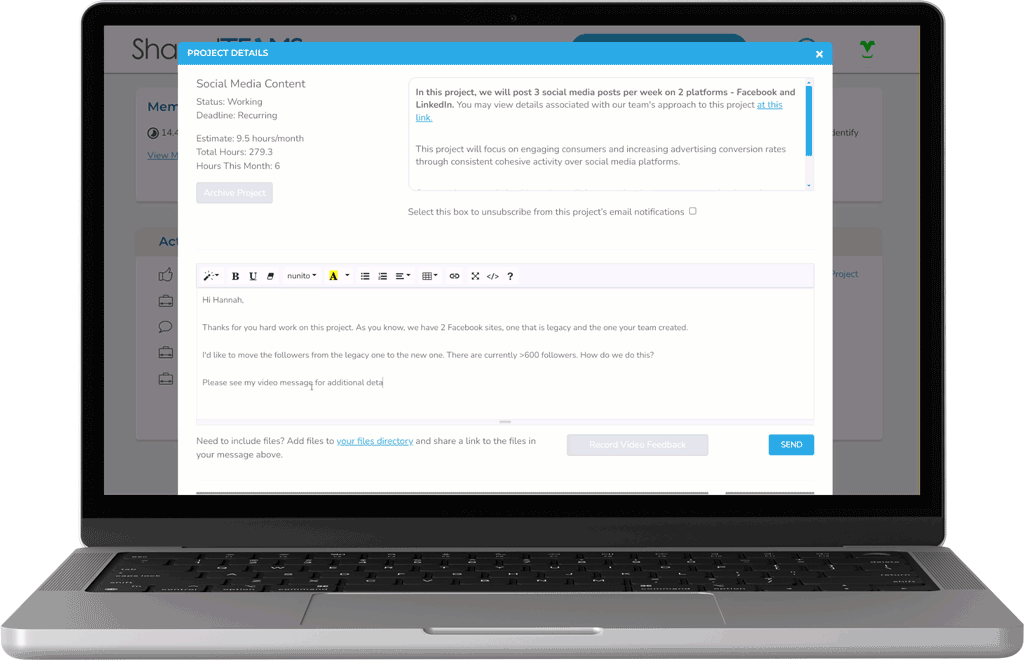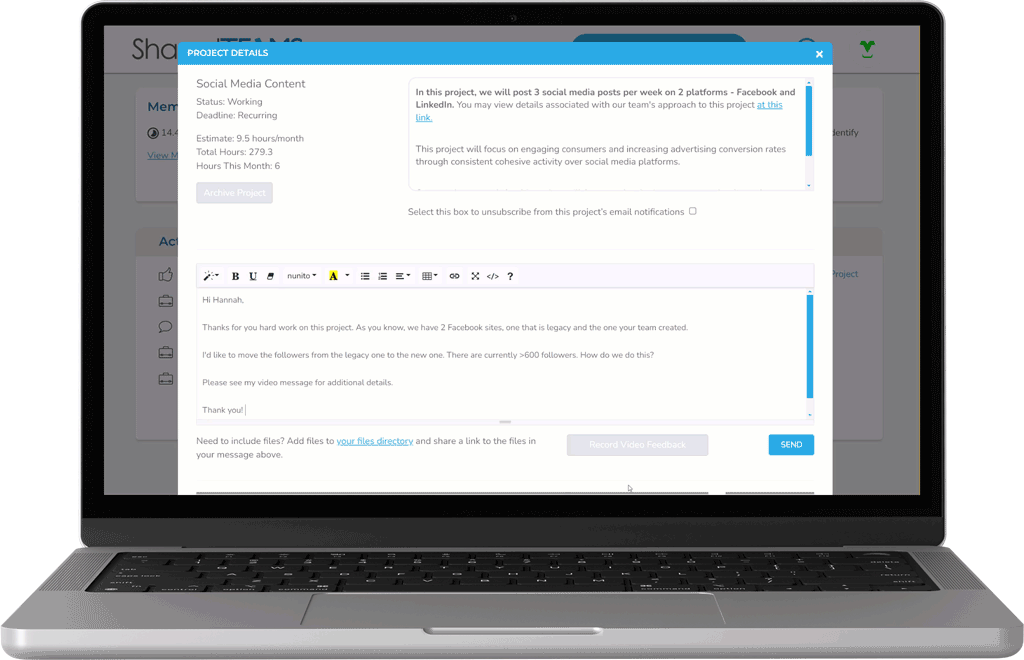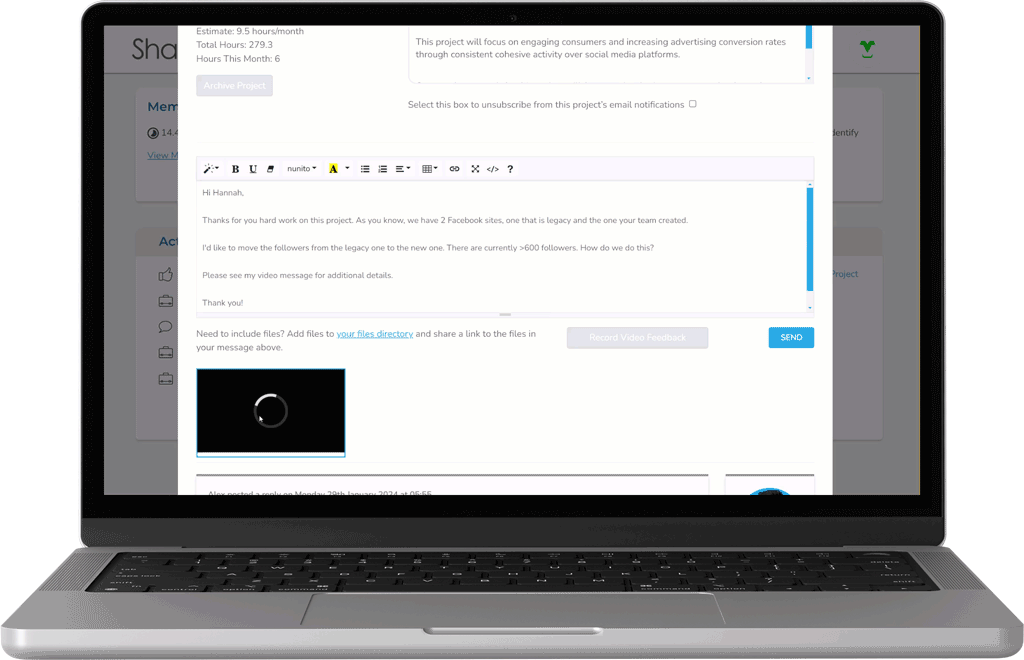
Control your Brand Guidelines
Our team is relentlessly brand-focused and fanatical about quality, with multiple layers of QA behind the scenes on every project.
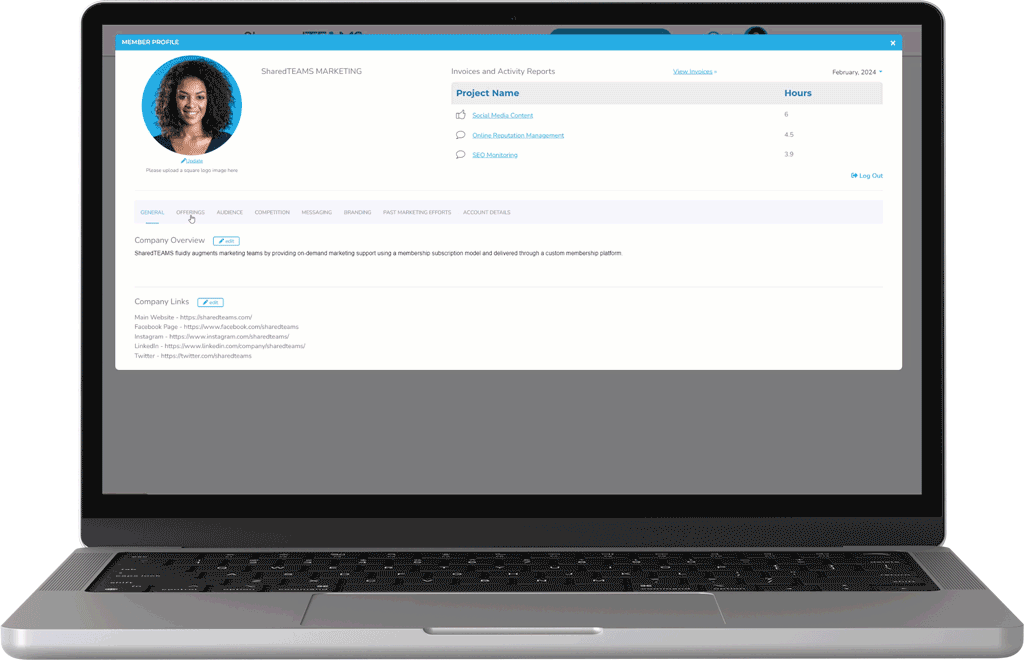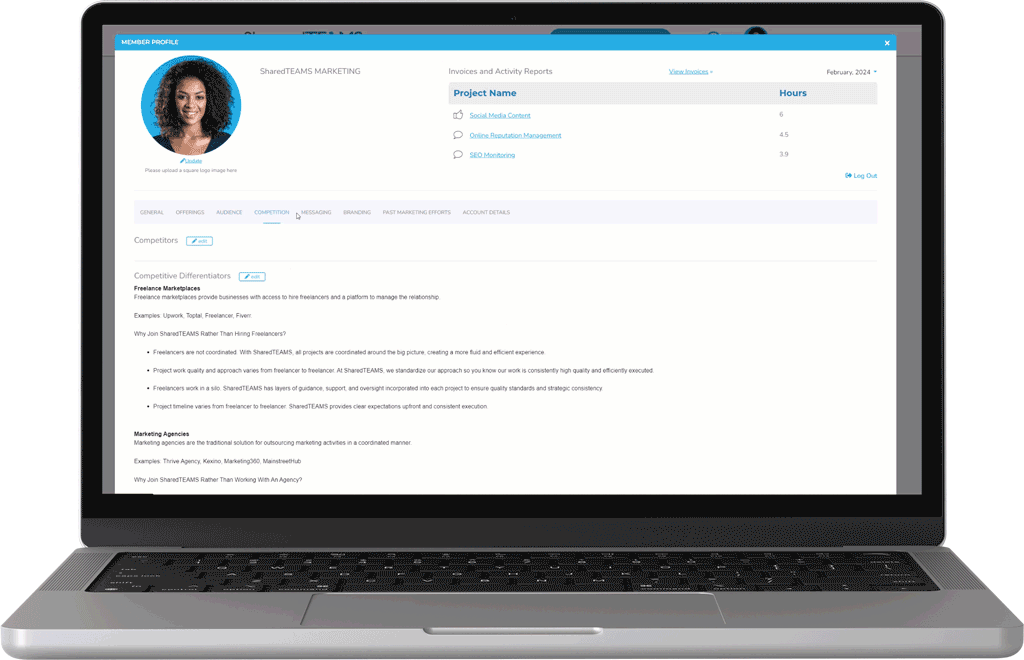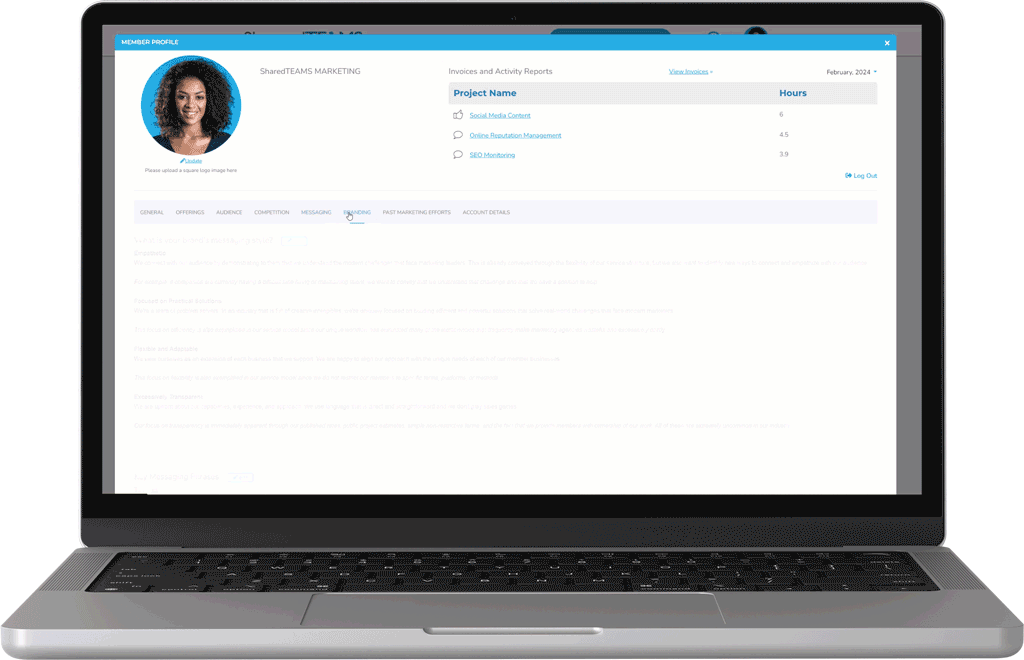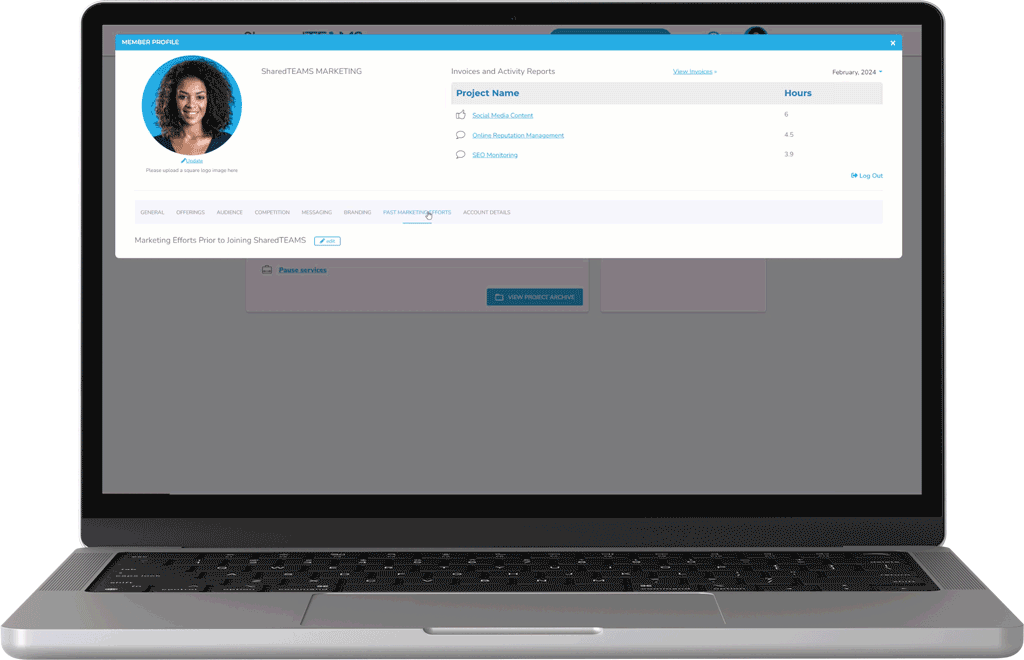

Member Success Stories
Learn how our team has helped hundreds of businesses across multiple industries solve complex marketing challenges since 2010.

A Shared Marketing Department
777 Brickell Ave
Suite 500-9662
Miami, FL 33131
800.670.5543
2443 Fillmore St
Suite 380-5552
San Francisco, CA 94115
800.232.0752
Copyright @ 2024 SharedTEAMS, LLC. All Rights Reserved.